Introduction
Cloud computing has evolved into a dynamic and transformative force, continually shaping the landscape of modern technology. This evolution is exemplified by the convergence of cutting-edge technologies and innovative strategies, creating a synergistic ecosystem and emerging trends and technologies are reshaping the way we approach business and technology solutions that also propels business into a new era of efficiency, security, and agility. Join us on this journey to discover how these emerging trends and technologies are revolutionizing the cloud computing landscape and opening up new possibilities for businesses across the globe.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Cloud Computing Trends
- 1. What is Cloud Integration?
- 2. What is Cloud Security and DevSecOps?
- 3. Multi Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud Strategies
- 4. What is Cloud Virtualization?
- 5. What is Cloud Containerization?
- TECHNOLOGIES
- 1. What is Service Mesh?
- 2. What is SASE?
- 3. What is Disaster recovery and VDIs ?
- 4. What is Cloud Migration?
- 5. How Cloud Orchestration works?
- 6. What is Green Cloud?
- 7. What is Cloud Region?
- Conclusion
Cloud Computing Trends
1. What is Cloud Integration?
Cloud integration refers to the process of connecting and synchronizing data, applications, and services that are hosted in cloud servers. This typically involves linking various cloud-based resources and platforms to work together seamlessly.
The integration of IoT, blockchain, AI, and ML into cloud computing creates a dynamic ecosystem for data-driven innovation. IoT sensors capture data from the physical world and transmit it to the cloud, where blockchain ensures secure, immutable data storage. Smart contracts, operating within the blockchain, automate predefined actions. Simultaneously, AI and ML algorithms process this data in real-time, providing actionable insights and predictive analytics.
This synergy empowers diverse industries, from predictive maintenance in manufacturing to telemedicine in healthcare. Cloud computing’s scalability and cost-efficiency support seamless data orchestration and analysis. The integration enhances transparency, enhances security, and enriches decision-making capabilities, paving the way for transformative applications.
2. What is Cloud Security and DevSecOps?
Cloud security is undergoing a revolutionary shift in cloud computing with the integration of DevSecOps principles, emphasizing security with cost effectiveness from design to deployment in cloud computing. DevSecOps represents a cultural shift, making security an inherent part of the entire development lifecycle. “Shift left” practices move security to earlier development stages, identifying vulnerabilities during coding and testing. DevSecOps fosters shared responsibility, with automated checks in CI/CD pipelines for real-time feedback and rapid vulnerability resolution. CI/CD streamlines software delivery, enabling continuous testing and deployment. Automated security assessments, like vulnerability scans and compliance checks, ensure only secure code reaches production.
3. Multi Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Multi-cloud and hybrid cloud computing strategies involve leveraging multiple cloud providers or combining private and public cloud computing resources. In a multi-cloud approach, organizations distribute workloads across various cloud computing platforms, reducing vendor lock-in and enhancing resilience. In a hybrid cloud setup, companies integrate on-premises infrastructure with public or private cloud resources, facilitating data sharing and workload portability. The process typically starts with a clear assessment of business needs and cloud compatibility, followed by designing and deploying appropriate cloud architectures. Ongoing management, monitoring, and optimization are essential to ensure efficiency, security, and cost-effectiveness in multi and hybrid cloud environments.
Here is a video for your understanding about the covered 3 trends by Bernard Marr, an International Author, Speaker and Social Media Influencer in Business and Technology landscape.
4. What is Cloud Virtualization?
Virtualization in cloud computing is a process that involves creating virtual instances of physical computing resources like servers, storage, and networks. This technology allows cloud providers to efficiently manage and allocate resources, providing numerous benefits to cloud environments.
The process begins with the use of a hypervisor or containerization platform. Hypervisors create and manage multiple virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server, while containerization abstracts and isolates applications into lightweight containers. These virtual instances can then be allocated to users based on their specific needs.
Virtualization in cloud computing improves resource use, reduces costs, and enhances security. It also enables quick resource scaling for increased flexibility.
5. What is Cloud Containerization?
Containerization, a game-changer in modern cloud computing development, has revolutionized how software applications are built, shipped, and deployed. At its core, containerization is about packaging applications and their dependencies into self-contained units known as containers. These containers are portable, consistent, and efficient, making them a cornerstone of modern cloud computing.
One of the key players in containerization is Docker. With Docker, developers can create containers that encapsulate their applications, ensuring they run consistently across different environments, from a developer’s laptop to a production server while leading to faster release cycles.
Containers have also opened the door to microservices architecture, where applications are broken down into smaller, independent services running in separate containers. This approach offers greater flexibility, scalability, and resilience.
To manage containers at scale, we turn to Kubernetes, a container orchestration platform. Kubernetes automates tasks like scaling, load balancing, and self-healing, making it easier to manage containerized applications in complex environments.
TECHNOLOGIES
1. What is Service Mesh?
Service mesh is a critical component in cloud computing, providing robust communication and control between microservices within a complex application. It abstracts networking complexities, offering features like load balancing, security, and observability. Mesh components, such as Envoy proxies, intercept and manage traffic, enabling resilience through retries and circuit-breaking. Service mesh helps with A/B testing, canary deployments, and blue-green releases. It enhances security with mTLS and fine-grained access control. Popular service mesh solutions like Istio and Linkerd simplify these capabilities. In summary, service mesh streamlines microservices communication, making applications more reliable, observable, and secure in cloud computing.
Here is a tweet by Rohit Ghumare, An Indian Software Engineer and Influencer known by DevOps Guy explaining the process.
– Istio’s identity management relies on X.509 certificates following the SPIFFE specification, enabling strong mTLS without application awareness.
– Istio-ingressgateway and Istio-egressgateway act as Envoy proxies configured to allow traffic into and out of the cluster. pic.twitter.com/OsSD2sRKu7— Rohit Ghumare | That #DevOps Guy✍️ (@ghumare64) September 18, 2023
2. What is SASE?
Secure Access Service Edge, (SASE) an emerging technological concept within cloud computing, effortlessly merges network security with cloud-native services. In this framework, the traffic of users’ networks is seamlessly directed through a cloud-based platform where security policies are applied dynamically. SASE combines Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) with vital security components such as firewalls, VPNs, and Zero Trust access, resulting in a cohesive and adaptable network security infrastructure. This strategy not only boosts adaptability but also trims hardware costs while ensuring consistent security measures across all endpoints, marking it as a transformative force in the era of remote work and cloud-centric strategies.
3. What is Disaster recovery and VDIs ?
Disaster recovery in cloud computing encompasses virtual desktops, crucial for uninterrupted business operations. The process includes data backups, automated replication, snapshots of virtual desktop configurations, load balancing, and automated failover setups. Network redundancy ensures continuous user access, even during outages. Regular testing and monitoring systems ensure the readiness of the recovery plan, detecting and addressing anomalies promptly. Integrating virtual desktops into your strategy is essential for maintaining seamless cloud-based operations during disasters, preserving critical resource access, and safeguarding against disruptions.
In a survey conducted by statista stated that “In 2022, the data center virtualization market recorded a revenue worth seven billion U.S. dollars. By 2030, the global application virtualization market is expected to exceed 23 billion U.S. dollars.”
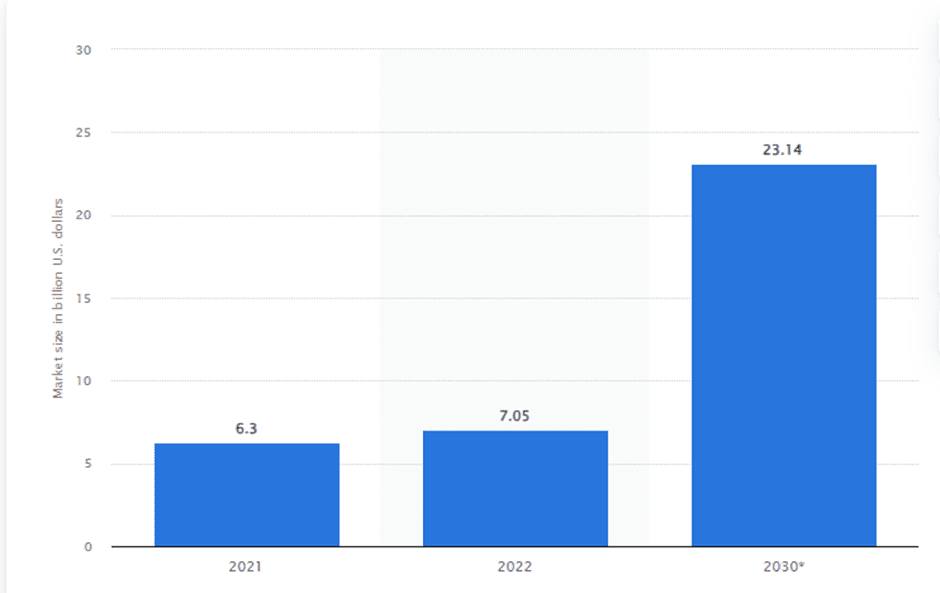
Credits: Statista
4. What is Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration with Cloud Volumes ONTAP, a powerful data management solution, optimizes the transition to the cloud. It begins with infrastructure assessment and ONTAP deployment in the chosen environment of cloud computing. ONTAP facilitates efficient data replication, reducing downtime. Its data transformation capabilities, such as deduplication and compression, cut storage costs. Seamless application integration ensures uninterrupted access, and thorough testing validates data integrity and performance. During cutover, ONTAP manages data redirection. Ongoing ONTAP-powered monitoring, backup, disaster recovery, compliance, and security measures ensure a smooth cloud transition with data and cost control, making ONTAP an indispensable asset in cloud computing migration.

Credits: WWT
5. How Cloud Orchestration works?
Cloud orchestration is the automated management of cloud computing resources and applications, streamlining complex workflows for scalability, reliability, and efficiency ensuring cost-effective operations. It begins with defining infrastructure as code (IaC), where resources are described in a script. Next, cloud computing orchestration tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation deploy and configure these resources, ensuring consistency. Then, application code is deployed using tools like Kubernetes or Docker Swarm, with continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines ensuring seamless updates. Monitoring and auto-scaling mechanisms maintain optimal performance, while logging and alerting provide insights into system health.
6. What is Green Cloud?
The term “Green Cloud” refers to environmentally conscious and energy-efficient practices within the realm of cloud computing. It focuses on reducing carbon emissions and resource consumption associated with data centers. This is achieved through the adoption of renewable energy sources, optimization of data center cooling mechanisms, and the use of energy-efficient hardware. The benefits of green cloud initiatives include environmental sustainability, cost savings, and a positive public image for organizations committed to eco-friendliness. As environmental concerns continue to rise, the adoption of green cloud practices is crucial for mitigating the tech industry’s environmental impact.
7. What is Cloud Region?
A cloud region represents a geographically specific area where a cloud service provider houses its data centers and infrastructure. These regions are strategically dispersed worldwide to ensure redundancy, minimize latency, and comply with data sovereignty regulations. Each region typically comprises multiple data centers or availability zones, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. Customers select a cloud region based on factors like proximity to users, disaster recovery needs, and data compliance requirements. Leading cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, and GCP offer multiple regions globally, allowing organizations to scale their services while optimizing performance and resilience.
Conclusion
The realm of cloud computing is witnessing a convergence of technologies and strategies that are reshaping the way businesses operate. From leveraging cutting-edge technologies like AI, IoT, blockchain, and ML to enhancing security through DevSecOps practices, optimizing resource allocation via virtualization and containerization, and adopting versatile multi-cloud and hybrid solutions, the cloud is at the forefront of innovation and efficiency. Service mesh and SASE are revolutionizing communication and security, while disaster recovery and cloud migration ensure seamless business operations. As cloud orchestration automates complex processes, organizations are primed to embrace the future with enhanced agility, resilience, and transformative capabilities.















