Introduction
Cybersecurity is a critical aspect of modern business operations, and staying informed about its key facts is paramount. In this rapidly evolving digital landscape, understanding these top 10 facts about cybersecurity facts is crucial for protecting sensitive data, ensuring regulatory compliance, and maintaining trust with partners and clients. From the role of AI and IoT in cyber threats to the importance of encryption and incident response plans, these facts are indispensable for safeguarding against ever-sophisticated cyberattacks in 2023 and beyond.
Discover all the interesting facts about Cybersecurity, for altering the face of modern business with us
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Enhancing B2B cybersecurity visibility
- Strategic Data Ownership
- Cybersecurity for SMEs
- API Security Readiness Assessment
- Enhancing Data security
- Cybersecurity for Critical Sectors
- Navigating Industry 4.0
- Financial Cyber Security Regulations
- Role of Cyber Security in B2B
- Digital Solutions of Cybersecurity
- Conclusion
Enhancing B2B cybersecurity visibility
Enhancing information visibility in B2B cybersecurity management is vital for proactive threat detection, cost-effective resource allocation, legal compliance, and mitigating risks. It ensures business continuity, builds trust, and provides a competitive edge. Improved visibility aids in safeguarding sensitive data, making informed decisions swiftly, and adapting to evolving cybersecurity needs. In an era of growing cyber threats, these facts about cybersecurity are indispensable for protecting data, reputation, and sustaining business operations efficiently.
Here is a tweet by IBM Security explains how can we prevent cyber attacks taught by IR Consultant
The key to preventing cyberattacks is learning from past incidents.
Listen to IR Consultant @cybersecmeg break down her role in helping organizations understand the root cause of incidents, along with custom strategies to protect against future attacks: https://t.co/ACR2kA5yPE pic.twitter.com/L6xvjUBIpZ
— IBM Security (@IBMSecurity) September 6, 2023
Strategic Data Ownership
Data ownership refers to the legal and ethical rights and responsibilities of individuals or organizations over the data they collect, generate, or control, including the ability to use, share, or restrict access to that data. Facts about Cybersecurity and Data ownership is a crucial aspect in the business world, especially when moving from traditional in-house software solutions to cloud based options. It’s clear that organizations can gain a competitive edge by maintaining exclusive data and smoothly incorporating data ownership into their strategic plans. Furthermore, with modern business environments and collaborative models, companies can enhance their data assets by sharing information within their strategic networks. This approach promotes innovation and helps build a sustainable competitive advantage.
Cybersecurity for SMEs
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) often lack a comprehensive understanding of cybersecurity risks and face internal challenges in developing effective cybersecurity strategies. To address this, a user-centric approach, visually mapping how people interact with technology to depict SME practices and threats.
By combining the Customer Journey Modelling Language (CJML) and the System Security Modeller (SSM), It is to raise awareness on facts about cybersecurity and improve communication among IT, security experts, and non-technical personnel. This approach demonstrates the compatibility of these methods and suggests potential for further validation in addressing cybersecurity threats within SMEs.
API Security Readiness Assessment
In the context of the growing use of APIs in B2B digital communications, robust API management and security programs are essential. Technology providers offer API management solutions, and established security standards ensure safe API transactions. APIs are vulnerable, examining perspectives from customers and cybersecurity vendors. Some research findings reveals within the facts about cybersecurity that API exploits often go unnoticed, and security readiness varies based on IT roles and identifies crucial concepts for enhancing API security management, emphasizing the importance of security in enabling open and straightforward API deployment for B2B and B2C communications. API exploits remains a challenge, emphasizing the need for improved detection mechanisms in this evolving landscape.
Enhancing Data security
As data is playing a pivotal role in every firm, it’s an essential strategy to protect data. For instance, The transformative impact of e-commerce on modern business practices has led to a heightened focus on cybersecurity measures. As we aware of e-commerce practices are crucial for their overall cyber resilience, requiring robust data protection measures like encryption and secure authentication as for known fact E-commerce sites play a crucial role in ensuring cybersecurity, particularly when it comes to protecting customer data. Proactive prevention of cybercrime is essential, requiring organizations to allocate resources to defend against potential intrusion attempts. Recommendations include integrating security features like complex passwords, data encryption, and multi-factor authentication, considering cybercrime insurance services, and conducting regular risk assessments.
Cybersecurity for Critical Sectors
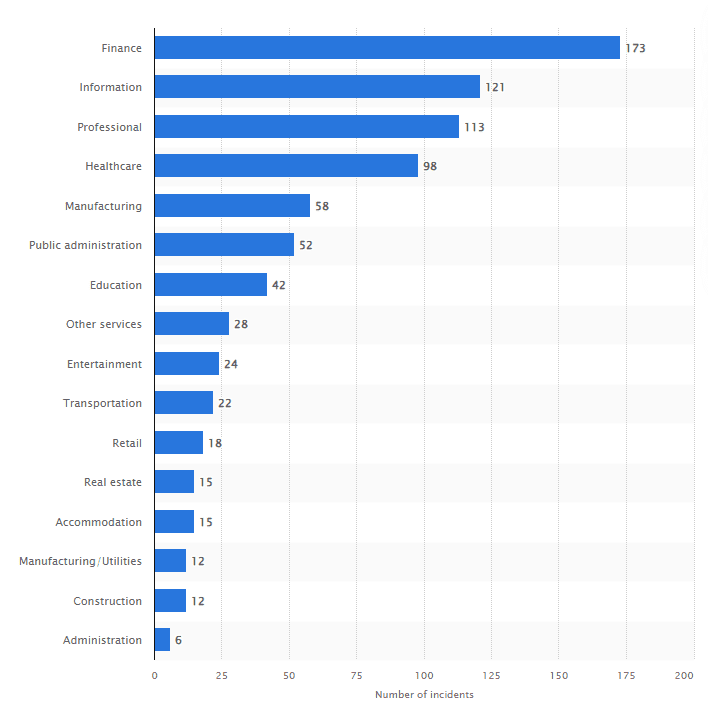
Government sites with classified data, financial institutions including UPI, and the healthcare sector are high-priority targets for cyber threats. These sectors store valuable information, making robust cybersecurity measures crucial. Security practices include firewalls, routine audits, employee training, data encryption, and incident response plans. Protecting these critical areas isn’t just about compliance; it’s vital for national security, financial stability, and public trust. Even for the Firms also. In an era where data holds immense value, proactive cybersecurity is the frontline defense against relentless cyberattacks.
As mentioned here, a survey from Statista says that the financial sector is the most targeted sector. According to a survey on global industry sectors, they were most targeted by basic web application attacks from November 2021 to October 2022.
In the context of Industry 4.0, cybersecurity has emerged as a critical concern due to the heavy reliance on integrated information systems and technology. With manufacturing companies depending on data to drive their operations, the increasing adoption of the Internet of Things has exponentially expanded the potential entry points for cyber threats. Complex digital value chains expose firms to risks beyond their direct control, making cyberattacks a substantial threat to business continuity, confidential information, and reputation. Despite the growing urgency, there is confusion among C-suite executives and entrepreneurs regarding how to address these complex issues. Cybersecurity professionals often struggle to convey the relevance of the issue to non-technical stakeholders.
Financial Cyber Security Regulations
The fintech industry operates under a stringent framework of regulations to ensure the security and privacy of sensitive financial information. Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data Security Standard (DSS) is a set of regulations aimed at safeguarding credit card data. It mandates secure handling, storage, and transmission of cardholder information. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a cryptographic protocol ensuring secure data transmission over the internet. These regulatory measures require organizations to implement SSL encryption for data in transit and adhere to PCI DSS compliance, which includes regular security assessments, network monitoring, and access control to protect sensitive payment card data, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring a safer digital payment environment.
Role of Cyber Security in B2B
Cybersecurity is essential for B2B growth, preserving trust, and compliance. It shields against data breaches, fostering trust with partners and clients. Regulatory adherence is vital in many industries. By prioritizing cybersecurity, businesses avoid legal issues and focus on innovation and expansion. In the competitive B2B world, cybersecurity distinguishes companies and ensures long-term success. In the competitive B2B landscape, cybersecurity distinguishes, ensuring long-term growth and success as thus builds client trust to the firm
Digital Solutions of Cybersecurity
In 2023, cybersecurity faces notable trends: AI’s role in both defence and increasingly sophisticated attacks, the IoT’s expanding attack surface, cloud computing’s security challenges, rising ransomware threats, and the persistence of insider risks. To stay secure, organizations must conduct regular assessments, implement layered security, educate employees, establish incident response plans, and stay informed about evolving threats. These proactive measures are essential for safeguarding data and mitigating cyber risks in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Conclusion
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity isn’t merely a choice; it’s a necessity. From enhancing B2B visibility to safeguarding critical sectors and adapting to emerging trends, prioritizing cybersecurity is the linchpin of success. As businesses navigate Industry 4.0 and the complexities of data ownership, they must remember that proactive measures not only protect data but also build trust, ensuring a secure foundation for innovation and growth in our interconnected world.
Partner with Sparity for all your Cybersecurity solution.















