Introduction
UX (User Experience) is a process that enhances user satisfaction by improving usability, accessibility, and overall delight in interaction between screens, designs, and users. It is primarily focused on the digital world, where screens are more frequently used.
The UX design Thinking Process is a problem-solving approach that involves understanding user needs, brainstorming creative solutions, and iteratively testing and refining prototypes to address complex challenges. Designing an interface is not as straightforward as commonly thought, and a positive UX requires extensive research, understanding user psychology, incorporating colour theories, visual design elements, and ensuring proper alignment.
Below are the 5 steps incorporated by One of the earliest and most influential models associated with design thinking is often credited to IDEO and Stanford University d.school.
Steps
Table of Contents
Empathize
A first and foremost step in UX design thinking process. Understanding the needs, feelings, and motivations of people is a necessary component of empathizing in UX. Gaining an understanding of user experiences and issues is the goal of this stage. Through observation and interviews, gain a deeper understanding of users’ goals, sentiments, and pain points in order to create design solutions that work.
Tools include personality types, empathy maps, surveys, observation, shadowing, and interviews. By empathizing with consumers, designers may gain a thorough grasp of their wants and pain spots and create solutions that really address those needs. When we empathize we can clearly gain insights into the user experience.
We say it with experience. With ‘#Empathy‘ as our core value, we’re able to bring technology innovation, employee efficiency, and customer satisfaction.#DesignThinkingProcess #DesignThinking #innovation #efficiency #satisfaction #designmethodology pic.twitter.com/o7IAm4gh63
— Techtic Solutions (@TechticSolution) July 30, 2021
Define
In order to define the issue precisely, the data acquired during the empathy step must be combined to continue the UX design thinking process. It involves rephrasing the design problem in terms of user needs. Integrate research to identify user demands and create a concise problem statement that serves as a precise and intentional guide for the design process. A clear direction for the design process can be established by clearly defining the challenge. It guarantees that the design team is focused on resolving pertinent issues and unites all project participants.
Tools include affinity diagrams, user journeys, problem statements, and statements of viewpoint.
Ideate
Design teams use ideation, a creative process, to come up with a wide range of potential solutions for a given challenge. It’s about promoting an unrestricted exchange of ideas in UX design thinking process. Its all about your thinking and visualization. Thinking creatively and unconventionally is encouraged by ideation. A wide range of viable options are produced at this stage, giving the design team an endless number of concepts to consider and develop. Create original, varied ideas by advancing a wide range of viewpoints to inspire original solutions that specifically answer the needs of people.
Tools include Storyboarding, SCAMPER, Crazy 8s, Mind Maps, Brainstorming, and Prototyping.
Prototype
In prototyping, the design concepts are modeled in a low-fidelity manner. These can be interactive prototypes that let consumers interact with a condensed version of the design, wireframes, or doodles. Transform concepts into concrete, testable forms and enable early user feedback to effectively and iteratively improve the user experience. It’s a crucial step in UX design thinking process that you cannot ignore.
Through prototyping, designers can test and visualize their ideas more quickly. Early user feedback collection aids in the design phase and allows for iteration prior to major resource investment.
Prototyping tools include Figma, Sketch, Adobe XD, wireframes, mockups, and sketches.
Watch the video to know what exactly prototypes are
Test
Testing is required in showing the prototypes to users in order to get their input. This could be accomplished by conducting interviews, usability testing, or other techniques to find out how users engage with the design. Testing verifies that the design solutions are sound and satisfy user needs. It offers perceptions of what functions well and what needs enhancement, directing subsequent alterations and improvements. Test prototypes with users, gathering insightful feedback to support design decisions and promote ongoing development for a user-focused and functional end design.
Tools or steps include Iterative prototyping, A/B testing, feedback sessions, usability testing, and user testing. It’s the final step in UX design thinking process must to complete to ensure validation.
Kano Model Emphasis in UX
Professor Noriaki Kano of the Tokyo University of Science published the Kano Model of Product Development and Consumer Satisfaction in Japan in 1984.
Features are divided into basic, performance, and enjoyment components by the Kano Model. In recent days people widely extended this model to UX design thinking process, Understanding features effects on user satisfaction aids in prioritizing them in user experience (UX). Basic demands have to be satisfied, performance characteristics boost contentment in a linear fashion, and joy aspects add exponential value. A well-rounded and significant user experience is guaranteed by incorporating the Kano Model.
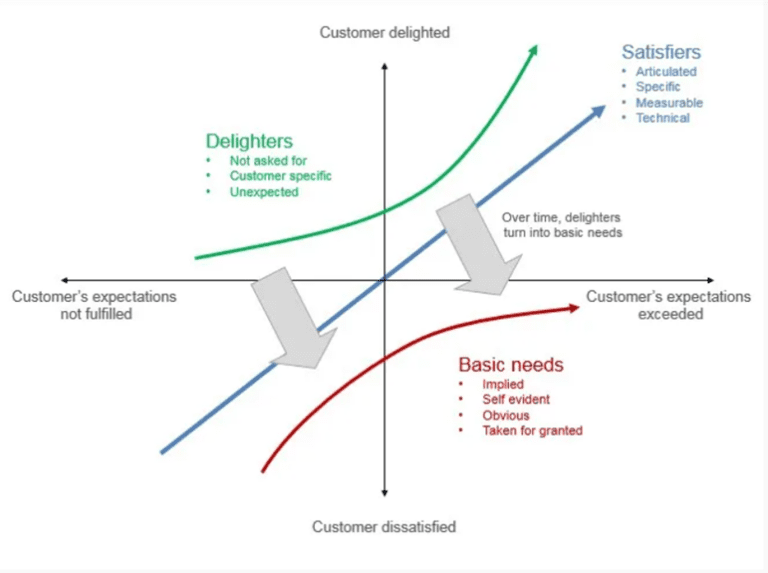
Picture Credits: Interaction Design Foundation
Attractive
Crafting attractive qualities in the context of UX design thinking process requires going above and beyond expectations to produce a delightful user experience. Beyond the basics, designers can innovate by adding unexpected elements that trigger intense emotions. While not essential, these are still valuable. Strategically using these characteristics increases user satisfaction and makes the design stand out. Acknowledging the affective significance of appealing attributes enables designers to establish a more profound connection with consumers, conforming to the compassionate foundation of UX design theory.
One-Dimensional
The one-dimensional aspect of UX design thinking process emphasizes the direct relationship between increased user experience and improved performance. Users satisfaction rises proportionately as designers improve efficiency and usability. User expectations are met by this consistent interaction, which creates a sense of reliability. When this approach is used, the result is a design that logically grows to meet user needs. One of the key principles of UX design thinking process is the one-dimensional quality, which highlights the significance of continuously enhancing design performance to meet and exceed user expectations.
Must-Be
The must-be addresses essential requirements of users as non-negotiable components in the UX design thinking process. These features are necessary for satisfaction and, in the absence of them, cause dissatisfaction. Prioritizing essential features and incorporating them smoothly provides the framework for a design that is focused on the user. This method recognizes how important these elements are for maintaining usability and reliability. Building a design that satisfies consumers fundamental expectations requires early identification and resolution of must-have features or elements, to get the best design.
Indifferent
In the UX design thinking process, identifying in-differentiates involves determining elements that hardly affect user satisfaction. Designers can more efficiently manage resources by knowing which elements don’t significantly affect the user experience. By focusing efforts on areas that really important, this understanding enables a streamlined design process that optimizes the user interface without needless complications or designs. Understanding indifferent characteristics improves the effectiveness and concentration of UX design ideas.
Reverse
Preventing user dissatisfaction requires addressing contrary features in the UX design thinking process. Improving the user experience as a whole requires identifying and fixing components that cause adverse reactions. Designers can remove or alter elements that, when present, cause discontent by applying empathic design thinking. By preventing possible problems and strengthening the bond between users and the design, this proactive approach ensures a more seamless and satisfying user experience.
Conclusion
We believe efficiency in designing comes from doing UX design thinking process more effectively, While technical expertise is crucial for a project, the first interaction users have is with the screens, not the code quality. Sparity prioritizes efficiency in designing and simplifying complexities, ensuring a seamless user experience through features that enhance search ease. There’s a saying that users form an impression within 8 seconds, and Sparity promises that the 8 months of hard work invested in a project will be evident and worthwhile in those critical first seconds with our UI/UX expertise.















